During a woman’s menstrual cycle her ovaries will develop a dominant follicle (or small sac) which contains an egg. Fourteen days after the start of a woman’s last period this follicle will have grown, the egg mature and is released (or ovulated). The egg then survives for about 24 hours during which time it moves into the fallopian tube and awaits fertilisation by sperm. This is a woman’s fertile time.
Clomiphene citrate ovulation induction
In women who do not ovulate by themselves, clomiphene may induce ovulation and allow women to conceive reasonably quickly without the need for more complex treatments.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) ovulation induction
Another form of ovulation induction uses subcutaneous (just under the skin) injections of the hormone FSH.
What is Intrauterine Insemination?
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is the placing of specially prepared concentrated “washed” sperm into the cavity of the uterus, bypassing the cervix. This is performed close to the time of ovulation (releasing of egg). IUI is a better, cheaper and easier alternative to try. It is recommended however, that after three unsuccessful attempts of IUI, consideration should be given to moving onto In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
Reason to consider IUI treatment
- Unexplained infertility
- Tubal disease – There should be at least one normal tube and ovary.
- Endometriosis – Intrauterine insemination is used for mild forms but not for severe endometriosis.
- Age – This procedure has been shown to have good success in women under 40 years of age.
- Mild sperm abnormalities – IUI is an effective treatment where there are minor sperm abnormalities.
- Psycho-social influences – Men who are away from their partners for extended periods of time may elect to have their sperm frozen and artificially inseminated whilst they are absent.
Insemination Process
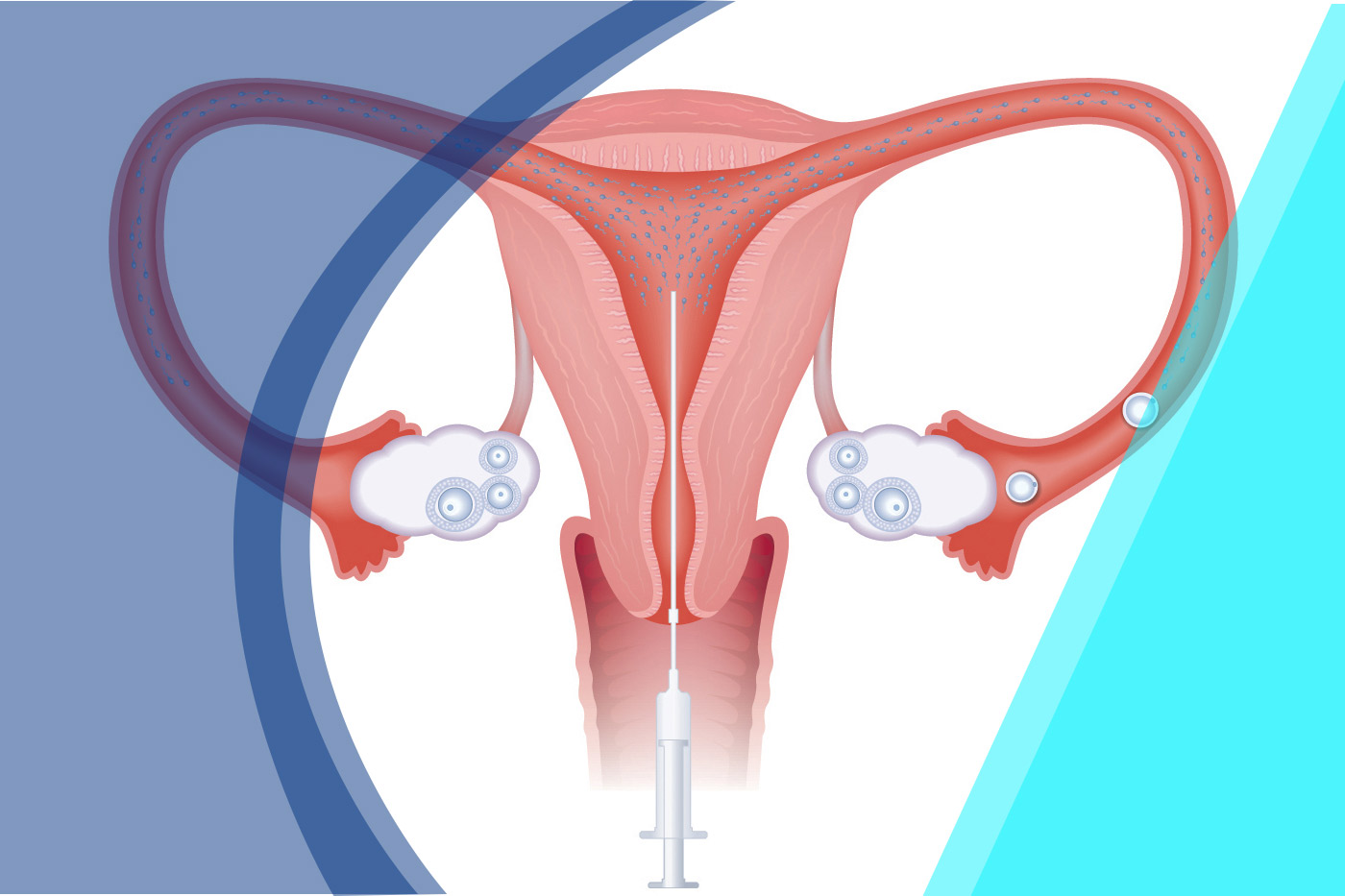
When the monitoring suggests the ovaries (and eggs) are ready, a final ‘triggering’ injection of hCG will cause ovulation. Insemination is planned to coincide with this, 36-48 hours later.
On the day of planned insemination, your partner needs to produce a sperm sample. Within two hours of the sperm being prepared, you will be inseminated at the Clinic. This simple procedure is usually not painful but some mild cramping discomfort may occurs. You can them get up immediately, return to work and go about your normal daily routine.
A serum hCG (pregnancy hormone) test will be performed 2 weeks later.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF is the original ‘ test-tube baby’ technique, and probably the most widely practiced assisted- conception procedure in the world. In simple terms, IVF removes several eggs from the ovary, fertilizes them in the laboratory with sperm from the male partner and transfers a small selection of the resulting embryos to the womb for implantation and pregnancy. Although IVF was developed to treat couples whose principal cause of infertility is tubal damage, the technique has also been found useful in those with endometriosis, sperm disorders (poor sperm counts or morphology) and even unexplained infertility. Studies indicate that the expectation of pregnancy from one cycle of treatment is around average 25 per cent in younger women (mid 20’s). However the pregnancy rate can go as high as 40% or even more (depending on condition of the women and IVF centre) and the chance of delivery slightly less. Overall, the average take-home baby rates from IVF is about 15 per cent for each cycle of treatment. These rates are not much different from those of normal fertile couples. Most studies have shown pregnancy rates falling in women after the age of 35, which is why many infertility specialists encourage couples to act quickly when the female partner is already in her early thirties.
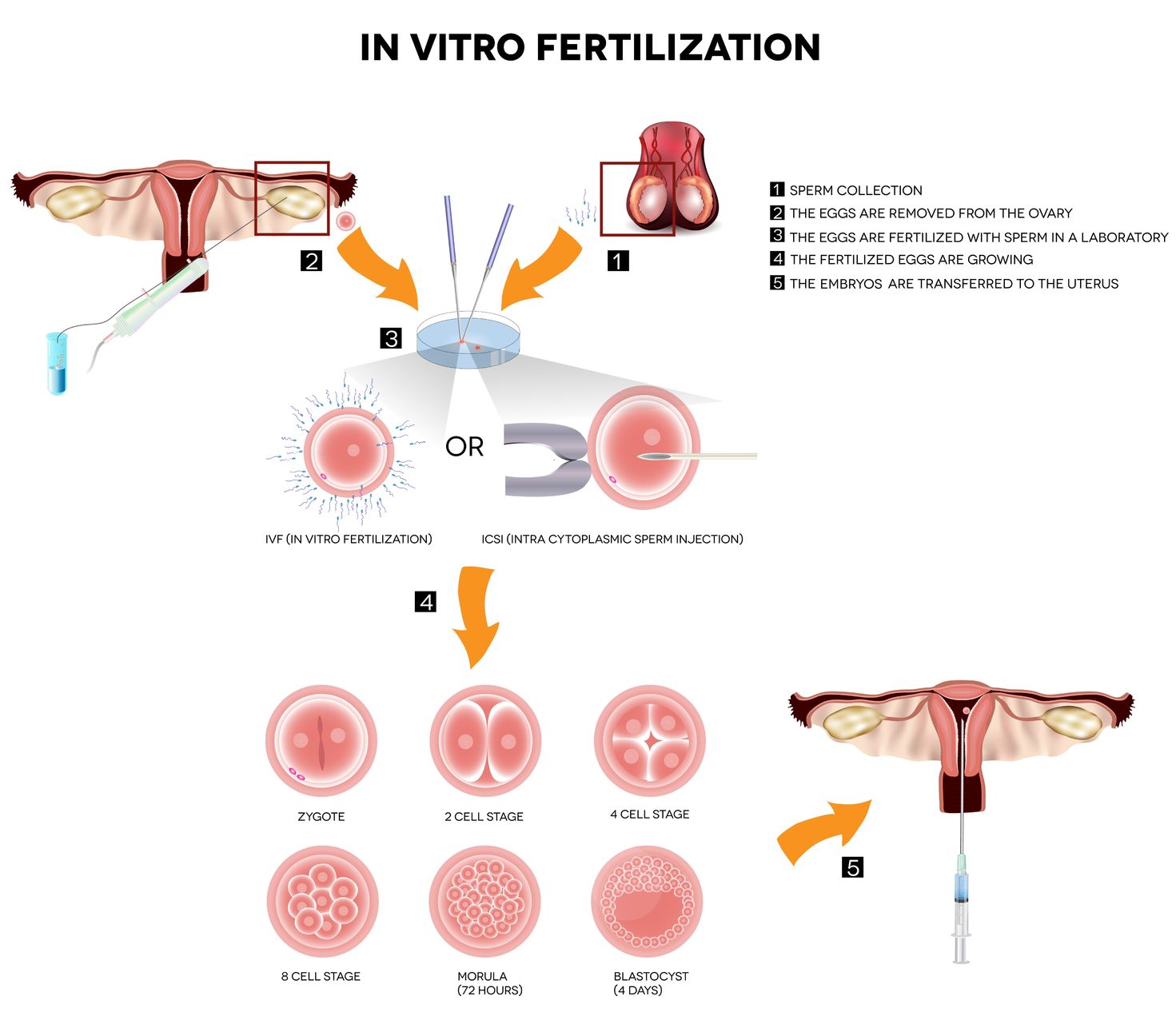
Process of IVF
- Drug treatment to stimulate several eggs to mature. GnRH agonist is used to suppress all other hormone activity (injections for usually two weeks before gonadotropins and then a further 10-14days depending on response). Alternatively, GnRH antagonist can be used to suppress all other hormones (as an agonist). However, this is started after the use of gonadotropins. The overall cycle length is reduced by 2 weeks by using GnRH antagonist. Gonadotropins is drug used to stimulate the growth of follicles and cause ovulation.
- Monitoring of treatment such as measuring the growth of follicles by transvaginal ultrasound scanning (two or three times during a treatment cycle), individualize drug doses and prevent serious side effects. Sometimes, blood sample will be collected to measure the hormones level.
- The procedure of egg collection will be performed 32-36 hours after final hormone injection. Egg collection is perform with the guidance of transvaginal ultrasound and it usually takes about 10-20 minutes under local anaesthesia.
- Sperm sample will be provided on the same day as egg collection.
- Fertilization will take place from eggs and sperm prepared and cultured together overnight. Eggs will be examined the next day under microscope.
- Transferring of Embryos (usually two or three days after fertilization). No more than three embryos will be transferred transvaginal and placed in the womb. Spare embryos will be frozen for any subsequent uses.
- Pregnancy test/ monitoring