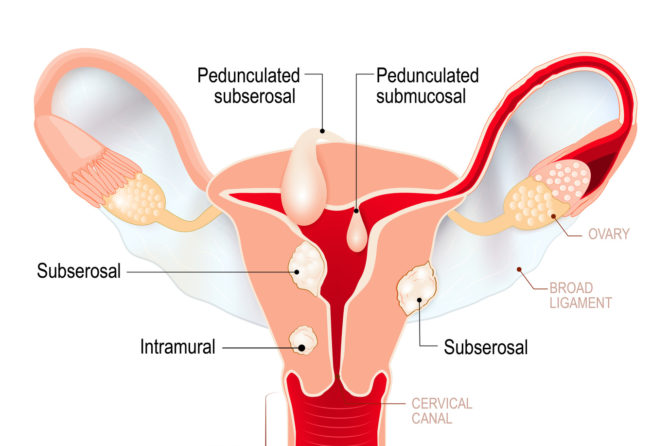
1. What are they?
Uterine Fibroids are muscle swellings that are found in the womb. They are usually not cancerous.
2. Who are affected?
Fibroids are very common in women. They occur in about 20% of women.
They are commonly found in women between the ages of 35-45 years old. They are more common in certain races like the West Indians and Africans.
3. What do they look like?
They can occur in many shapes and sizes, single or multiple located in various parts of the womb.
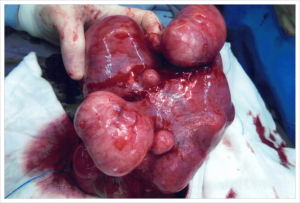
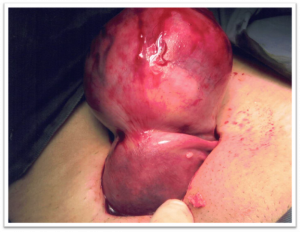
4. What kind of problems can they give to women who have them?
Most women with fibroids have no problems.
In other cases, fibroids can cause heavy menstrual bleeding or menstrual cramps or both.
If they are large, you can sometimes feel them in your abdomen or when the doctor examines you. Sometimes, they can put pressure on the surrounding organs like the bladder or the kidneys, giving rise to difficulty in voiding.
Some women may have problems in conceiving.
5.Who is most likely to have fibroids?
Fibroids are most common in women aged 30-40 years, but they can occur at any age. Fibroids occur more often in African American women than in white women. They also seem to occur at a younger age and grow more quickly in African American women.
6. How are fibroids diagnosed?
They can be found either by clinical examination or by ultrasound scanning.
7. How are fibroids treated?
a. Do nothing-
If the fibroids are not giving any problems, the doctor may advise that all you need to do is to be checked up regularly to monitor any changes in the size.
b. Medication –
This can be given to shrink the size of the fibroids but does not make them disappear. This is usually given before an operation so that surgery will be less difficult. This is not a long term solution.
Medication such as GnRH agonists can also be given temporarily to control the symptoms such as painful or heavy period.
Currently, there is a medical treatment with ulipristal acetate that can be used to shrink fibroids but this is not permanent.
c. Surgery is offered when symptom is not controlled with medication or fibroids are too big/ growing too quickly.
There are two types of operation:
If the woman still wants to conceive, then the fibroid will be removed only (myomectomy). This can be done laparoscopically or by abdominal approach. If the woman has completed her family and is having lots of problems with the fibroids, then the womb is removed (hysterectomy). This is done laparoscopically or by abdominal approach.
In conclusion, fibroids are non-cancerous muscular swellings found commonly in the wombs of women. They can cause various problems, are easily diagnosed and treated accordingly.
Leave a reply