What is Endometriosis?
Endometriosis is the presence of endometrial tissue outside the cavity of the uterus. It is most commonly found in the ovaries (chocolate cyst), fallopian tubes, tissues that hold the uterus in place and outer wall of the uterus. Rarely, it may be found in the other body sites such as the lungs, rectum, etc.
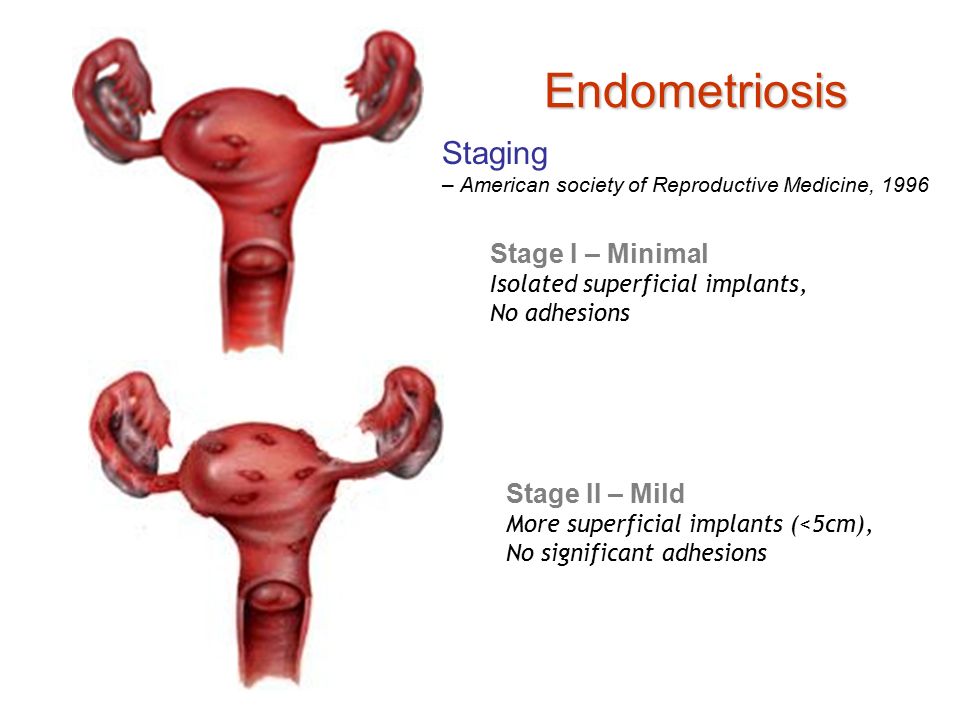
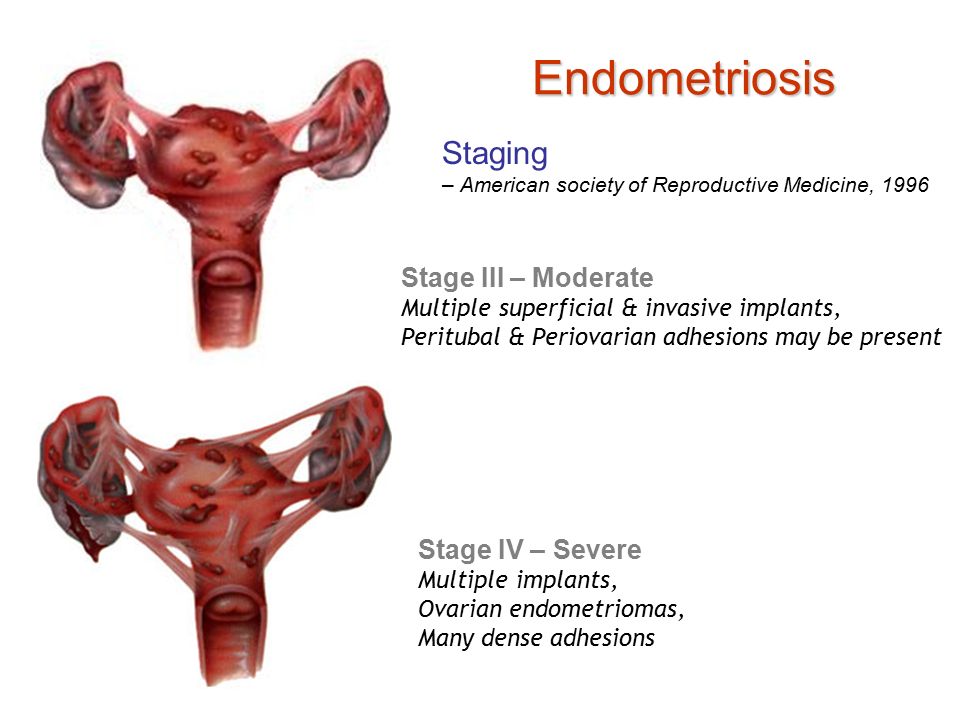
Like the endometrium of the uterus, this tissue also grows and bleeds every month leading to inflammation, swelling and scar tissue formation. Your doctor may use stages to describe the severity of endometriosis.
How common is Endometriosis?
One out of every 10 women of childbearing age (from the start of periods to menopause) suffers from endometriosis. The risk is higher in women who:
- Have shorter monthly cycles (more periods per year)
- Have periods lasting for more days
- Began getting periods at an early age
- Have a close relative (mother, sister) with endometriosis
What are the cause of Endometriosis?
The exact cause of endometriosis is not known. Various theories have been put forth.
- Retrograde menstruation
- During menstruation, some menstrual blood flows backwards through the fallopian tubes into the pelvis
- The endometrial cells get attached to the pelvic structure resulting in endometriosis
2. Lymphatic or circulatory spread
- The endometrium gets into the blood and the lymph vessels and is transported to other sites
3. Coelomic metaplasia
The cells that cover the ovary get converted into the endometrial cells.
- Immune abnormality
- Hormonal abnormality
Whatever the cause of endometriosis, its growth is controlled by the female sex hormones.
What are the symptoms of Endometriosis?
Most women consider pain during periods as normal. However, you may have endometriosis if you have:
- Severe pain during periods that interferes with daily activities.
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
- Pain during or after sex
- Pain or bleeding on passing stools
- Pain or bleeding on passing urine
- Low back pain
Some women do not have any symptoms and are diagnosed for infertility.
Can Endometriosis affect sex life?
More than 50% of women with endometriosis experience pain during and after sex. In some women, pain occurs with certain positions and deep penetration. This can adversely affect the relationship with your partner and can cause anxiety and depression. By taking the right treatment and discussing the problem with your partner, you can lead a normal sexual life with endometriosis.
Can Endometriosis cause infertility?
Over years, scar tissue may form around the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This can lead to obstruction and blockage of fallopian tubes resulting in infertility. In fact, endometriosis is the main cause of infertility in more than one-third of women. However, with the right treatment, you can become pregnant even if you have endometriosis.
How is Endometriosis diagnosed?
The most preferred way to diagnosed endometriosis is laparoscopy. In this procedure, the inside of your pelvis can be examined by an instruments called laparoscope (inserting probes with keyhole openings made in you abdomen). This procedure is done under anaesthesia. Biopsies of suspected endometrial tissue may be taken during laparoscopy.
Ultrasound or Computed Tomography (CT) scans may also be advised by your doctor.
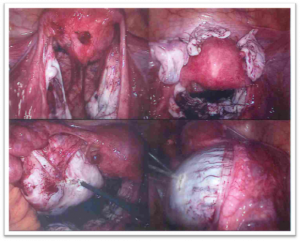
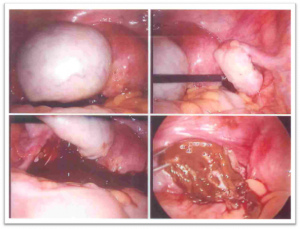
What are the various ways to treat Endometriosis?
There is no absolute cure for endometriosis. However, with treatment, pain and other symptoms may be alleviated. Treatment of endometriosis depends on:
- Symptoms
- Stage of disease
- Desire to have children
- Age
Endometriosis can be managed both by medical and surgical method:
- Pain medication for mild symptoms
- Hormonal therapy such as GnRH (Lucrin Depot), oral contraceptives, progestins and danazol in women who do not wish to become pregnant.
Women who have extensive endometriosis, severe pain and problems with fertility may need surgery.
- Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus)
- Laparoscopy
- Removal of endometrial tissue